Digital Transformation in Education
Digital Transformation in Education
Introduction
Over the last decade, there has been a significant overhaul with the advent of fast-track technology in the education sector. Digital transformation in education means the incorporation of digital technologies meant to enhance learning experiences, improve operational efficiency, and create a far more inclusive and accessible education system. From the online learning platforms to AI-based personalized education, digital transformation is remolding the traditional educational landscape into a new shape, creating a framework for more efficient learning experience.
The Need for Digital Transformation in Education
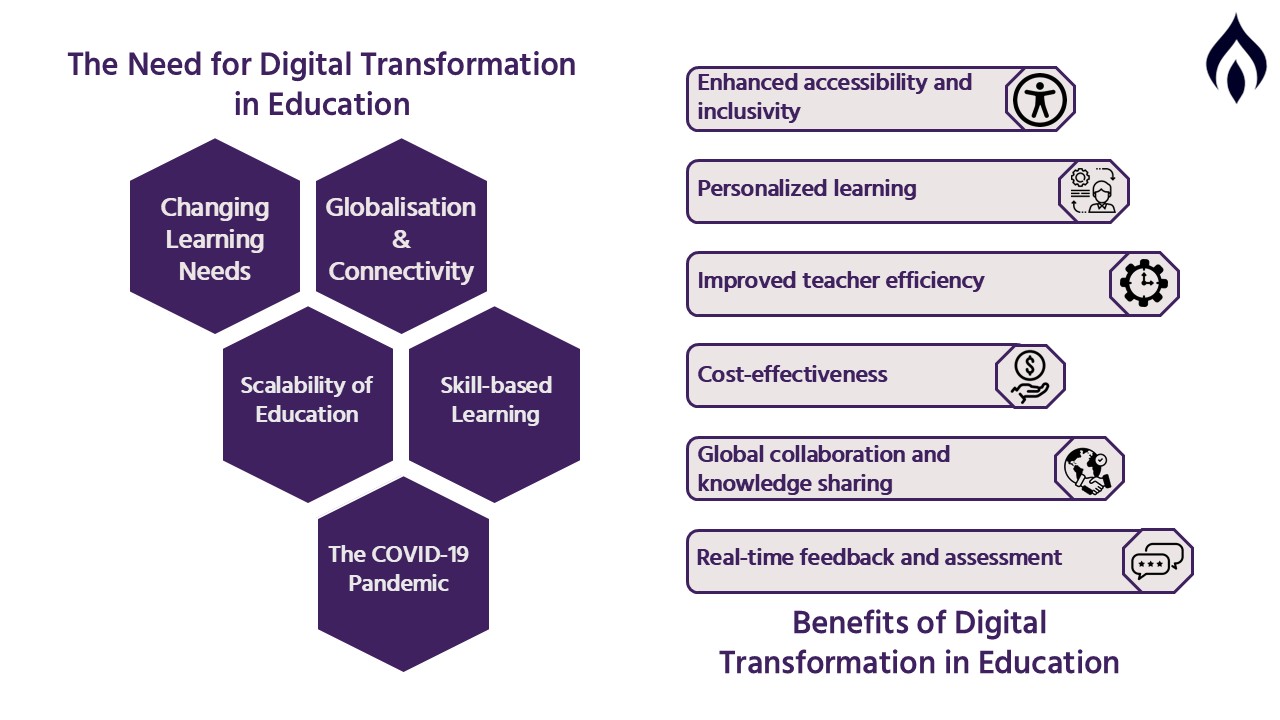
Several factors have contributed to the growing need for digital transformation in education:
- Changing Learning Needs: Today’s learners prefer interactive, engaging, and flexible learning environments that can meet their varied learning preferences.
- Globalization and Connectivity: The rise of globalization and connectivity has enabled students to collaborate with peers worldwide, allowing educational institutions to adopt a business strategy that leverages digital tools for seamless learning.
- Scalability of Education: Traditional educational institutions have found accommodating more students these days quite a task against the digital environment, which seems to host a better scalable option.
- The COVID-19 Pandemic: The onset of the pandemic acted as a spur in the acceleration of online education and use of digital tools, underscoring the absolute need for a technology-adaptable education.
- Skill-based Learning: The requirement for digital skills and technical skills has escalated, and the education system needs to weave modern technological proficiencies into its training.
Key Technologies Driving Digital Transformation
Several emerging technologies are playing a crucial role in transforming education:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI-enabled tools personalize learning experiences by analyzing student performance and customizing content according to their needs. AI-based chatbots, virtual tutors, and automated grading systems are enhancing the efficiency of learning. With the adoption of AI and IoT (Internet of Things), smart classrooms are integrating real-time monitoring systems that improve learning outcomes and operational efficiency.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS)
LMS platforms like Moodle, Blackboard, and Google Classroom allow educators to create, manage, and deliver digital courses. These systems allow remote learning and streamline course administration.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR & AR)
Combining VR and AR has permitted students to learn science and history in nebulous parameters such as on-the-job training or solid field practice, hence making classes serious. Through virtual simulations, students can conduct lab experiments and explore historical sites, but without physically being on-site.
- Big Data and Learning Analytics
Data analytics have been employed by learning institutions to track student progress, identify learning gaps, and develop data-driven frameworks for personalized learning paths. Big data assists in the decision-making process, optimizes curriculum design, and predicts student success.
- Cloud Computing
Cloud-based platforms allow students and teachers to access learning materials remotely, so there is little or no dependence on physical infrastructure. Collaboration tools, such as Google Drive and Microsoft Teams, make communication and sharing common materials very easy, allowing institutions and companies in the ed-tech sector to provide services worldwide.
- Blockchain Technology
Blockchain assures secure and tamper-proof credential verification, which is crucial for corporate training programs and financial transparency in education systems. It also allows decentralized educational records to be created.
- Gamification and Adaptive Learning
Gamification techniques, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, make learning engaging. Adaptive-learning platforms change the level of difficulty based on a student’s progress, forming a roadmap for personalized learning experiences.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Education
- Enhanced accessibility and inclusivity.
Digital learning erases geographical and financial boundaries, giving students from remote and disadvantaged areas a chance to study. Assistive technology supports disabled students in such a manner that education becomes inclusive.
- Personalized learning.
Elements of AI and adaptive learning tools comprise a custom platform tailored to a student’s learning speed and preferences. This fosters student engagement and comprehension.
- Improved teacher efficiency.
Technology has taken over tedious administrative tasks such as grading, attendance recording, and course management, freeing the teacher to really focus on teaching and nurturing.
- Cost-effectiveness.
Digital education will reduce overhead in terms of physical infrastructure, print materials, and transport, optimally making education affordable for students and institutions alike.
- Global collaboration and knowledge sharing.
With online platforms, students and teachers can collaborate across borders, participate in international projects, and share their ideas with the entire world.
- Real-time feedback and assessment.
Technology allows feedback on student performance to be immediate, allowing timely intervention and support. AI analytics also informs educator decision-making, greatly influencing learning outcomes.
Challenges in Digital Transformation
Although its importance has been in every sense a need, digital transformation in education is facing numerous challenges:
- Digital Divide and Inequality
Not all learners have ready access to high-speed Internet, digital devices, reliable electricity, and proper training, producing unconscionable inequality in opportunities available for digital education.
- Resistance to Change
Traditional educators and institutions may become stuck in their routines, denying resistance to embracing new technologies despite many reasons ranging from unfamiliarity, training, and fear of job loss.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Educational institutions collect a lot of student data; thus, they remain most vulnerable to cybercity. After that, there is an often-confusing cat and mouse chase between maintaining the confidentiality and security of student’s data as something that must come first as a priority.
- Quality Control and Accreditation
The boom in online courses and calls for digital certification seeks credible quality assurance mechanisms that render these trusted bodies for recognition.
- Technological Infrastructure and Maintenance
Rebuilding digital infrastructure and maintaining the same is effortful and expensive, as to them, an option is to consider upgrading while keeping in mind the low budgets of the institutions.
Future of Digital Transformation in Education
Future education will be intertwined very deeply with technology. Some advance developments that one can hear of include these:
- AI-enabled smart classrooms with facial recognition to track student engagement.
- Lifelong learning platforms provide flexible, skill-oriented courses for CPD.
- Decentralized education models run on blockchain and peer-to-peer learning networks.
- Integration of metaverse learning environments, where students engage in virtual classrooms and simulations.
Conclusion
Digital transformation in education is more than just a trend; it is the future. By utilizing emerging technologies, education can develop into an even more personalized, readily accessible, and efficient space. Nevertheless, closing the gap on the digital divide, security of data, and change resistance is essential in establishing this digital education domain that benefits all learners equally. With the growth in technological knowledge, harnessing the power of digital transformation is critical as it articulates the future of learning and prepares students for the demands of the digital economy.

Add a review
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *